DIAGNOSTICS
An accurate diagnosis is the first step.
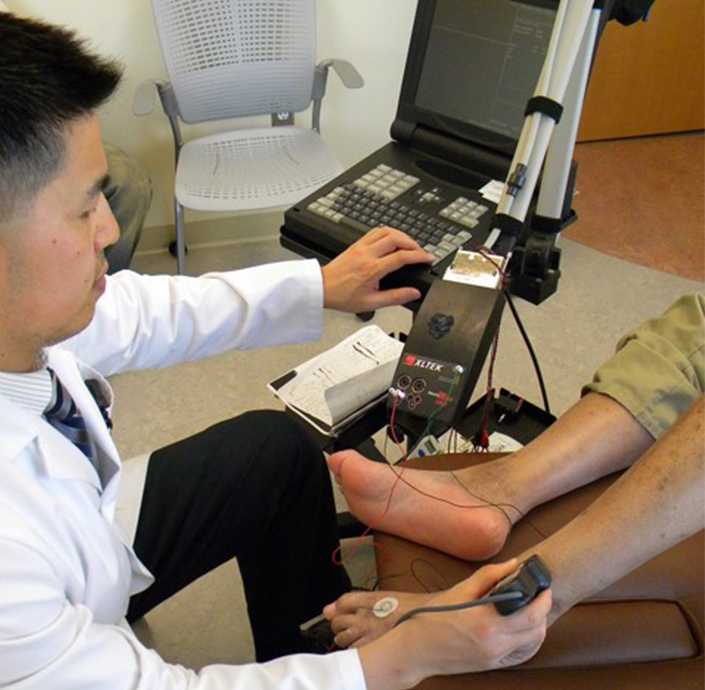
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
EMG and NCS are used to diagnose numbness, tingling, pain and weakness. EMG involves a fine needle inserted into a muscle to determine if any electrical signals are present at rest and then determine their pattern when activating the muscle. NCS involves harmless electric shocks which activate nerves followed by assessment of the size and speed of their signals on a computer screen.
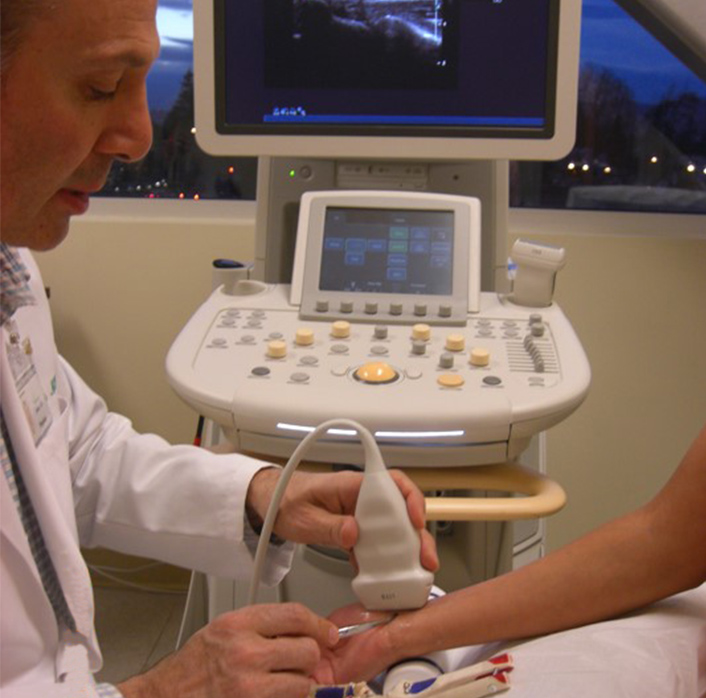
Musculoskeletal Ultrasonography
Musculoskeletal ultrasound is painless and involves placing some gel on the skin and using a transducer to scan nerves, muscles, tendons, ligaments and bony surfaces. Musculoskeletal ultrasonography is special and unique because it allows the doctor and patient to work together to determine which anatomical structures are tender and the source of pain.
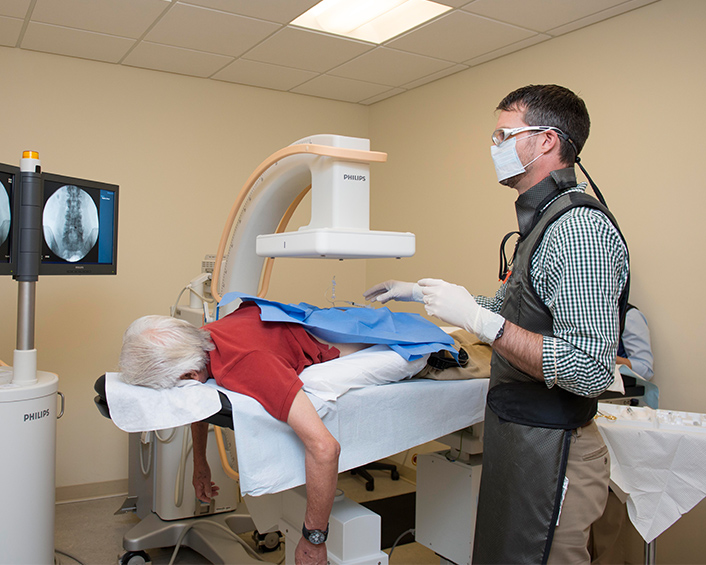
Local Anesthetic Blocks
Anesthetic blocks are the best way of determining the exact source of pain when imaging studies are not definitive or there are multiple possible pain generators. Without an accurate diagnosis, a successful treatment cannot be guaranteed. For example, if someone has pain in the groin, it could be from the hip or the spine. If a local anesthetic injection into the hip completely and temporarily relieves the pain, then the problem stems from the hip.
